Jakob Jenkov 2020-01-15
阻塞队列是一种在以下两种情况下会“阻塞”操作的队列:
- 当你尝试从一个**空队列中出队(dequeue)**时,操作会被阻塞,直到有其他线程向队列中插入元素;
- 当你尝试向一个**已满的队列中入队(enqueue)**时,操作也会被阻塞,直到有其他线程从队列中移除一个或多个元素,或者清空整个队列,从而腾出空间。
下图展示了两个线程通过一个阻塞队列进行协作的情形:
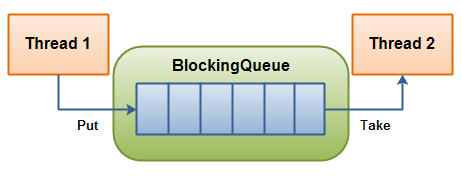
一个线程向
BlockingQueue中放入元素,另一个线程从中取出元素。
Java 5 在 java.util.concurrent 包中提供了阻塞队列的实现。你可以在 java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue 中了解更多相关内容。
即使 Java 5 已经内置了阻塞队列的实现,了解其背后的实现原理仍然非常有用。
阻塞队列的实现
阻塞队列的实现方式与有界信号量(Bounded Semaphore) 类似。下面是一个简单的阻塞队列实现:
public class BlockingQueue {
private List queue = new LinkedList();
private int limit = 10;
public BlockingQueue(int limit) {
this.limit = limit;
}
public synchronized void enqueue(Object item) throws InterruptedException {
while (this.queue.size() == this.limit) {
wait();
}
this.queue.add(item);
if (this.queue.size() == 1) {
notifyAll();
}
}
public synchronized Object dequeue() throws InterruptedException {
while (this.queue.size() == 0) {
wait();
}
if (this.queue.size() == this.limit) {
notifyAll();
}
return this.queue.remove(0);
}
}
请注意,在 enqueue() 和 dequeue() 方法中,只有当队列大小达到边界条件(即大小为 0 或等于上限 limit)时,才会调用 notifyAll()。
这是因为:如果队列既不是空也不是满,那么就不可能有线程正在等待执行入队或出队操作,因此无需唤醒任何线程。