Jakob Jenkov 发布于 2015-09-30
环形缓冲区是一种用作队列的数组。它包含一个读位置和一个写位置,分别标记下一个要从中读取和写入的位置。当写位置到达数组末尾时,会重置为 0;读位置同理。这种“回绕”(wrapping around)的行为使数组表现得像一个环,因此得名“环形缓冲区”。
本教程将解释环形缓冲区的工作原理,并展示两种 Java 实现方式。
环形缓冲区的工作原理
环形缓冲区是一个固定大小的数组,类似于有界队列。数组中存储着缓冲区中的元素。
除了元素数组外,环形缓冲区还包含:
- 写位置(write position):指向下一个要插入元素的位置。
- 读位置(read position):指向下一个要读取元素的位置。
- 已用/空闲空间信息:用于判断缓冲区是否满或空。
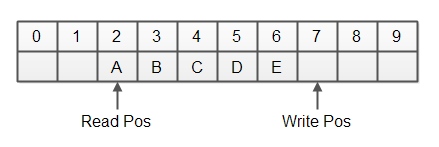
情况一:写位置尚未回绕
此时,已用空间位于读位置到写位置之间,其余为空闲空间。
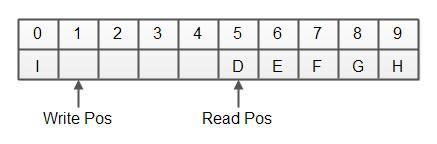
情况二:写位置已经回绕
此时,空闲空间位于写位置到读位置之间,其余为已用空间。
有多种方式跟踪读写位置和缓冲区状态。下面将介绍两种 Java 实现方式。
环形缓冲区为何高效?
环形缓冲区是实现类队列结构的一种高效方式——既易于实现,又性能出色。
使用场景
- 实际的队列(如消息队列)
- 数据生产者-消费者模型(流式处理)
- 需要严格限制缓冲区最大容量的场景
如果不需要容量上限,可考虑使用链表,或支持动态扩容的环形缓冲区(在满时分配更大的数组并迁移数据)。
本教程仅关注有界环形缓冲区。
实现技巧
本文介绍两种简单高效的实现方式:
- 使用填充计数(Fill Count)
- 使用翻转标记(Flip Marker)
基于填充计数的实现
该方法维护:
writePos:下一个写入位置available(即 fill count):当前缓冲区中元素数量
读位置通过 writePos - available 动态计算。若结果为负,则加上缓冲区容量。
public class RingBufferFillCount {
public Object[] elements = null;
private int capacity = 0;
private int writePos = 0;
private int available = 0;
public RingBufferFillCount(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.elements = new Object[capacity];
}
public void reset() {
this.writePos = 0;
this.available = 0;
}
public int capacity() { return this.capacity; }
public int available() { return this.available; }
public int remainingCapacity() { return this.capacity - this.available; }
public boolean put(Object element) {
if (available < capacity) {
if (writePos >= capacity) {
writePos = 0;
}
elements[writePos] = element;
writePos++;
available++;
return true;
}
return false;
}
public Object take() {
if (available == 0) {
return null;
}
int nextSlot = writePos - available;
if (nextSlot < 0) {
nextSlot += capacity;
}
Object nextObj = elements[nextSlot];
available--;
return nextObj;
}
}
基于翻转标记的实现
该方法显式维护:
readPos:下一个读取位置writePos:下一个写入位置flipped:标记写位置是否已回绕
元素数量根据是否翻转分别计算:
- 未翻转:
writePos - readPos - 已翻转:
capacity - readPos + writePos
public class RingBufferFlipMarker {
public Object[] elements = null;
public int capacity = 0;
public int writePos = 0;
public int readPos = 0;
public boolean flipped = false;
public RingBufferFlipMarker(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.elements = new Object[capacity];
}
public void reset() {
this.writePos = 0;
this.readPos = 0;
this.flipped = false;
}
public int available() {
if (!flipped) {
return writePos - readPos;
}
return capacity - readPos + writePos;
}
public int remainingCapacity() {
if (!flipped) {
return capacity - writePos;
}
return readPos - writePos;
}
public boolean put(Object element) {
if (!flipped) {
if (writePos == capacity) {
writePos = 0;
flipped = true;
if (writePos < readPos) {
elements[writePos++] = element;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
} else {
elements[writePos++] = element;
return true;
}
} else {
if (writePos < readPos) {
elements[writePos++] = element;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
public Object take() {
if (!flipped) {
if (readPos < writePos) {
return elements[readPos++];
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
if (readPos == capacity) {
readPos = 0;
flipped = false;
if (readPos < writePos) {
return elements[readPos++];
} else {
return null;
}
} else {
return elements[readPos++];
}
}
}
}
性能对比
- 单元素操作:基于填充计数的实现略快(但差距极小)。
- 批量操作:两种实现均显著优于单元素操作(吞吐量最高提升 4 倍)。
- 批量性能:基于翻转标记的实现比填充计数快约 15%。
批量操作因减少方法调用开销,在紧凑的数组复制循环中效率更高。
批量操作实现
填充计数版(含批量操作)
public class RingBufferFillCount {
// ...(字段与构造函数同上)
public int put(Object[] newElements) {
return put(newElements, newElements.length);
}
public int put(Object[] newElements, int length) {
int readPos = 0;
if (this.writePos > this.available) {
if (length <= this.capacity - this.writePos) {
for (; readPos < length; readPos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos++] = newElements[readPos];
}
this.available += readPos;
return length;
} else {
// 需同时使用数组顶部和底部空间
int lastEmptyPos = writePos - available;
for (; this.writePos < this.capacity; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos] = newElements[readPos++];
}
this.writePos = 0;
int endPos = Math.min(length - readPos, capacity - available - readPos);
for (; this.writePos < endPos; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos] = newElements[readPos++];
}
this.available += readPos;
return readPos;
}
} else {
int endPos = this.capacity - this.available + this.writePos;
for (; this.writePos < endPos; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos] = newElements[readPos++];
}
this.available += readPos;
return readPos;
}
}
public int take(Object[] into) {
return take(into, into.length);
}
public int take(Object[] into, int length) {
int intoPos = 0;
if (available <= writePos) {
int nextPos = writePos - available;
int endPos = nextPos + Math.min(available, length);
for (; nextPos < endPos; nextPos++) {
into[intoPos++] = this.elements[nextPos];
}
this.available -= intoPos;
return intoPos;
} else {
int nextPos = writePos - available + capacity;
int leftInTop = capacity - nextPos;
if (length <= leftInTop) {
for (; intoPos < length; intoPos++) {
into[intoPos] = this.elements[nextPos++];
}
this.available -= length;
return length;
} else {
// 复制顶部
for (; nextPos < capacity; nextPos++) {
into[intoPos++] = this.elements[nextPos];
}
// 复制底部(从0到writePos)
nextPos = 0;
int leftToCopy = length - intoPos;
int endPos = Math.min(writePos, leftToCopy);
for (; nextPos < endPos; nextPos++) {
into[intoPos++] = this.elements[nextPos];
}
this.available -= intoPos;
return intoPos;
}
}
}
}
翻转标记版(含批量操作)
public class RingBufferFlip {
// ...(字段与构造函数同上)
public int put(Object[] newElements, int length) {
int newElementsReadPos = 0;
if (!flipped) {
if (length <= capacity - writePos) {
for (; newElementsReadPos < length; newElementsReadPos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos++] = newElements[newElementsReadPos];
}
return newElementsReadPos;
} else {
// 写入顶部
for (; this.writePos < capacity; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos] = newElements[newElementsReadPos++];
}
// 写入底部
this.writePos = 0;
this.flipped = true;
int endPos = Math.min(this.readPos, length - newElementsReadPos);
for (; this.writePos < endPos; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[writePos] = newElements[newElementsReadPos++];
}
return newElementsReadPos;
}
} else {
// free space: writePos 到 readPos
int endPos = Math.min(this.readPos, this.writePos + length);
for (; this.writePos < endPos; this.writePos++) {
this.elements[this.writePos] = newElements[newElementsReadPos++];
}
return newElementsReadPos;
}
}
public int take(Object[] into, int length) {
int intoWritePos = 0;
if (!flipped) {
// 可用空间: readPos 到 writePos
int endPos = Math.min(this.writePos, this.readPos + length);
for (; this.readPos < endPos; this.readPos++) {
into[intoWritePos++] = this.elements[this.readPos];
}
return intoWritePos;
} else {
if (length <= capacity - readPos) {
// 直接从顶部复制
for (; intoWritePos < length; intoWritePos++) {
into[intoWritePos] = this.elements[this.readPos++];
}
return intoWritePos;
} else {
// 复制顶部
for (; this.readPos < capacity; this.readPos++) {
into[intoWritePos++] = this.elements[this.readPos];
}
// 复制底部
this.readPos = 0;
this.flipped = false;
int endPos = Math.min(this.writePos, length - intoWritePos);
for (; this.readPos < endPos; this.readPos++) {
into[intoWritePos++] = this.elements[this.readPos];
}
return intoWritePos;
}
}
}
}
并发安全性
- 上述两种实现均非线程安全,仅适用于单线程。
- 单生产者-单消费者场景下,基于翻转标记的实现更易改造为线程安全版本(因读写位置分离)。